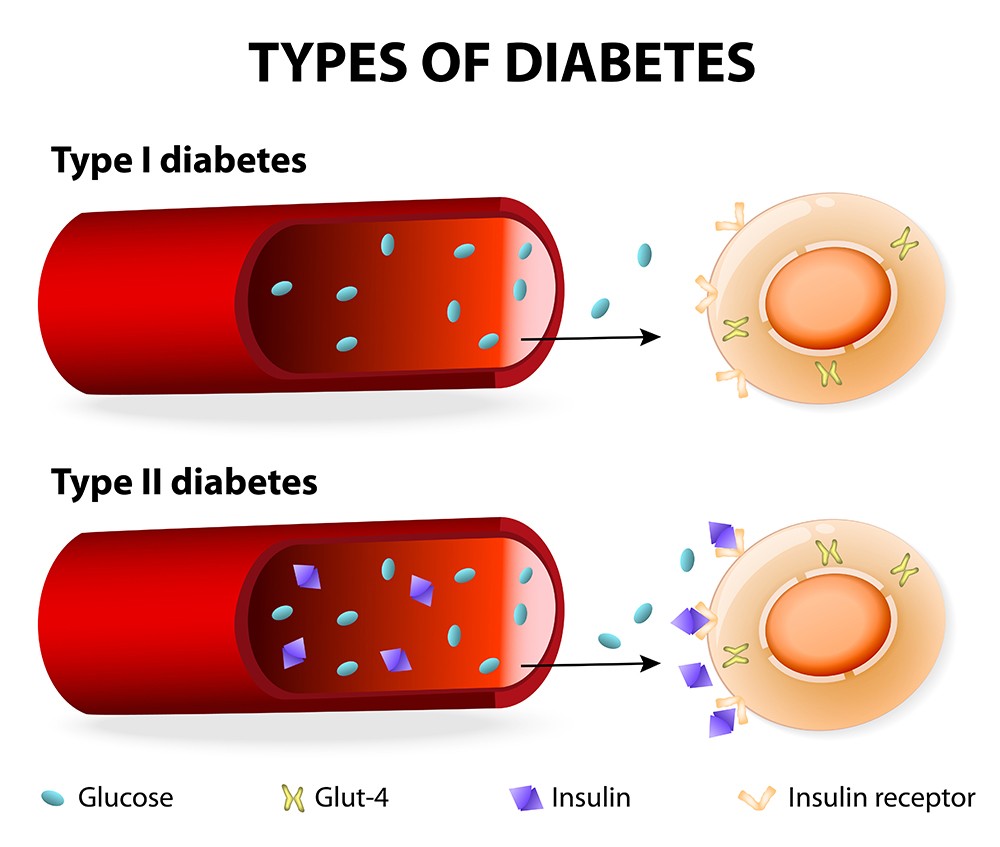
Diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the body is unable to produce insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors, and is characterized by the body’s inability to properly use insulin.
Table of Contents
Blood Sugar Fasting Range
The normal blood sugar fasting range is between 70 and 99 mg/dL. Fasting blood sugar levels higher than this may indicate pre-diabetes or diabetes. A fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or higher is considered diagnostic for diabetes.
Monitoring blood sugar levels
To monitor blood sugar levels, a person with diabetes may use a glucose meter, a small device that measures the amount of glucose in a drop of blood. A person with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels at regular intervals, as directed by their healthcare provider, to help manage their condition.
Type 2 diabetes and lifestyle factors
Type 2 diabetes is strongly linked to lifestyle factors, such as being overweight or obese, having a sedentary lifestyle, and poor diet. Research has shown that losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and increasing physical activity can improve blood sugar control in people with type 2 diabetes and even lead to the remission of the disease.
Reversing Diabetes
It is possible to reverse type 2 diabetes through lifestyle changes. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and getting regular exercise are all important steps in reversing diabetes. Additionally, some medications, such as metformin, can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
Diet and diabetes
Eating a healthy diet can help people with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels. A healthy diet for diabetes includes:
- Eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Choosing lean protein sources, such as fish, chicken, and beans
- Limiting added sugars, saturated and trans fats, and sodium
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water
Physical activity and diabetes:
Regular physical activity is important for people with diabetes as it can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, on most days of the week. Additionally, resistance training and strength exercises can help build muscle and burn calories.
Medications and diabetes
There are several medications available to help people with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels. These include:
- Metformin: a medication that improves insulin sensitivity and lowers blood sugar levels
- Sulfonylureas: a class of drugs that stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin
- DPP-4 inhibitors: a class of drugs that improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels
- GLP-1 receptor agonists: a class of drugs that improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels
Complications of diabetes
People with diabetes have an increased risk of developing several serious health complications, including:
- Cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attack and stroke
- Kidney disease
- Nerve damage, or diabetic neuropathy
- Eye damage, including diabetic retinopathy
- Skin conditions, such as diabetic dermopathy and necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum
Prevention of diabetes
To prevent type 2 diabetes, it is important to adopt a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and getting regular exercise.
Additionally, individuals who have a family history of diabetes or who have risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or a sedentary lifestyle should be screened for diabetes regularly by a healthcare professional.
Moreover, certain population groups such as older adults, individuals of certain ethnicities, and those with a history of gestational diabetes are also at increased risk for type 2 diabetes and should be screened accordingly.
Managing diabetes
Managing diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes monitoring blood sugar levels, taking medications as prescribed, eating a healthy diet, and engaging in regular physical activity. It’s also crucial to have regular check-ups with a healthcare professional and to be aware of any potential symptoms of complications.
Moreover, it’s important to have support from friends, family, or a support group, and to educate oneself on the disease and how to manage it. Additionally, managing other health conditions that often co-occur with diabetes, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and obesity can help improve overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a serious chronic disease that affects millions of people around the world. Managing blood sugar levels is essential for people with diabetes to avoid complications. However, it is possible to reverse type 2 diabetes through lifestyle changes and sometimes with medication.
Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and following the instruction of a healthcare provider, are crucial to managing diabetes and improving the quality of life.
In addition, preventing the disease is crucial as well, it’s important for individuals to be aware of their risk factors, to get screened, and to make lifestyle changes accordingly. Preventing type 2 diabetes can greatly reduce the chances of developing complications and improve overall health.